Slack Enterprise Secure Collaboration Use Cases
Skyhigh CASB for Slack Enterprise supports the following features to secure user collaboration.
- Identify and remove sensitive content shared with unauthorized guest users.
- View Slack incident metadata to monitor the shared file in public/private/shared channels.
- Monitor and Remove Guest Users joining the Slack channels from an unauthorized domain.
NOTE: The secured collaboration use cases are supported only for the Slack Enterprise version.
Identify and Remove Sensitive Content Shared with Unauthorized Guest Users
Skyhigh CASB for Slack Enterprise allows security admins to define the DLP policies to monitor and remove sensitive data posted in Slack channels having unauthorized guest users as members. Messages or files posted in the regular channels and 1:1 or 1: many chat conversations are monitored and deleted.
For example, say your organization has the domain myorg.com. Some of the Slack channels in MyOrg allows guest users as members. So the organization wants to detect and remove any sensitive data such as credit card numbers posted in channels that allow guest users.
To identify and remove the sensitive content posted in channels with guest users, define the DLP policy for Slack in the Skyhigh CASB as described.
Rule Group
Create the Collaboration for files and folder rule.
To create a Collaboration for files and folders:
- Go to Policy > DLP Policies.
- Click Actions > Sanctioned Policy > Create New Policy.
- On the Description page, enter a name, description, and deployment type. For Services, select Google Drive. Then select the users the policy will apply to.
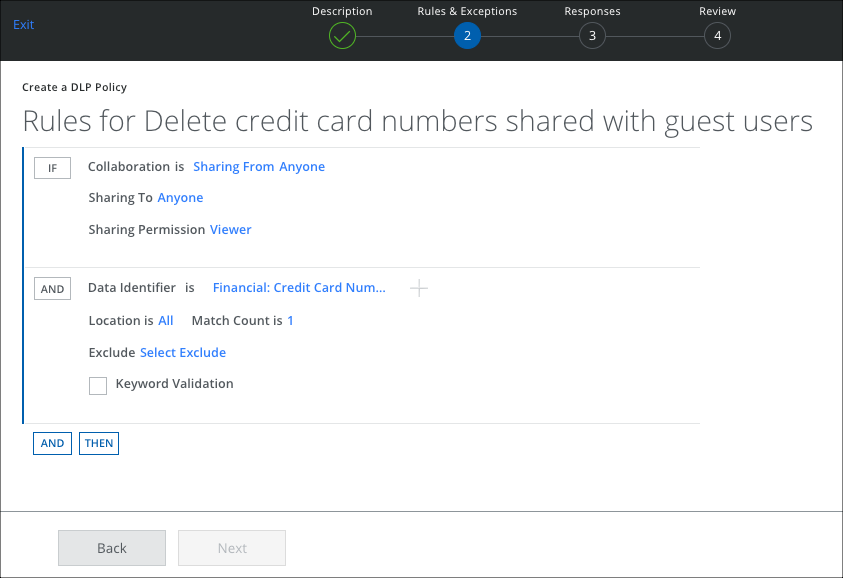
- On the Rules page, select Collaboration.
- For Sharing From, select Anyone.
- For Sharing To, select Anyone.
- For Sharing Permission, make a selection.
- Click AND and select any rule options such as Data Identifier, Keyword, or Regular Expression.
Exception Group
To add an exception to a policy:
- Click Add Exception.
- Select Collaboration.
- For Sharing From, select Anyone.
- For Sharing To, select Specific Users/Domains and Manually enter users/domains. Enter the domain names, for example, internal-domain1.com, internal-domain2.com, etc. In this case, the internal domain of the organization is myorg.com.
- For Sharing Permission, make a selection.
- Click Next.

Response Action
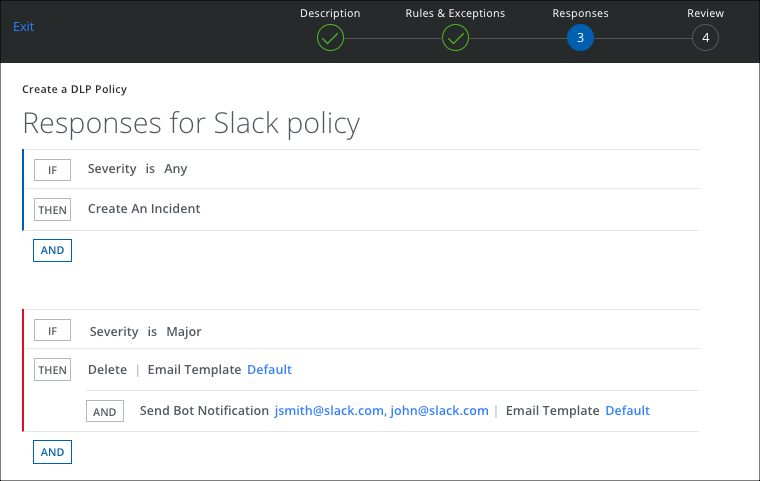
To add a response action to a policy:
- On the Response page, click AND, and select Delete to remove the sensitive data.
- Also select Send Bot Notification and enter the Slack User Email to notify the user about the DLP policy violation, or add a comma-separated list of email addresses.
- Select an Email Template.
- Click Next.
- Review your policy and click Save.
View Slack Incident Metadata for Shared Files
Let's say you have shared a file with a member in Slack. You can forward the same file to a public or private channel, by direct message, or by sharing a link. Any member with access to that file can also share it with others. So you can track the file shared with other members using Slack Incident Metadata.
To view the Slack Incident Metadata:
- Go to Incidents > Policy Incidents.
- Select Service Name as Slack from the filter.
- On the Policy Incidents page, click the required incident in the table to see the metadata in the Details pane.
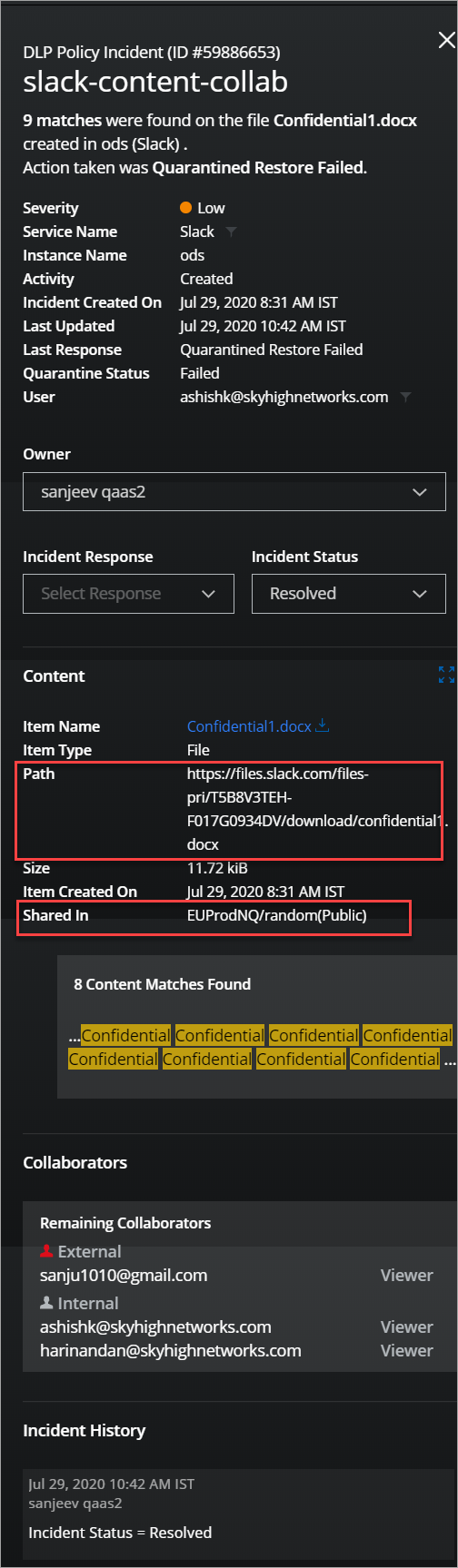
- Slack Incident metadata displays the following attributes to track the file-sharing activities:
- Path. The unique path of the file in Slack.
- Shared In. The name of the workspace / the channel name where the file is shared and displays the channel type (Public/Private).
Monitor and Remove Guest Users from Unauthorized Domains
Skyhigh CASB for Slack Enterprise allows security admins to define DLP policies to monitor and alert if any unauthorized guest users join the Slack channels.
For example, say you have an organization that wants to allow guest users from allowed domains allowed-domain1.com and allowed-domain2.com, but wants to alert if any guest or external users from other domains join the Slack channel. This can be accomplished by defining DLP policies for Slack in Skyhigh CASB.
Rule Group
To create a Collaboration for Files and Folders:
- Go to Policy > DLP Policies.
- Click Actions > Sanctioned Policy > Create New Policy.
- On the Description page, enter a name, description, and deployment type. For Services, select Slack. Then select the users the policy will apply to.
- On the Rules page, select Collaboration.
- For Sharing From, select Anyone.
- For Sharing To, select Anyone.
- For Sharing Permission, make a selection.

Exception Group
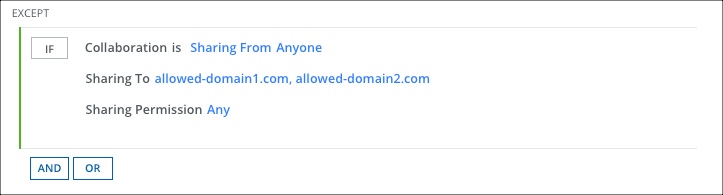
To add an exception to a policy:
- Click Add Exception.
- Select Collaboration.
- For Sharing From, select Anyone.
- For Sharing To, select Specific Users/Domains and Manually enter users/domains. Enter the domain names, for example, allowed-domain1.com, allowed-domain2.com, etc. If any guest user joins Teams from outside of the listed domains, then the policy is triggered.
- For Sharing Permission, make a selection.
- Click Next.
Response Action
To add a response action to a policy:
- On the Response page, click AND and select Revoke Sharing for and Everyone to remove the guest user.
- Select Send Bot Notification and enter the user's email addresses in a comma-separated list.
- Select an Email Template.
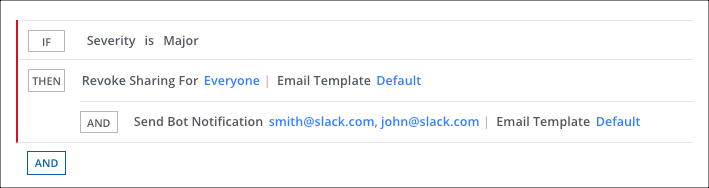
- Click Save.
- If any external user joins Slack channels by violating the DLP policy, then the DLP incident is created in the Policy Incidents page.
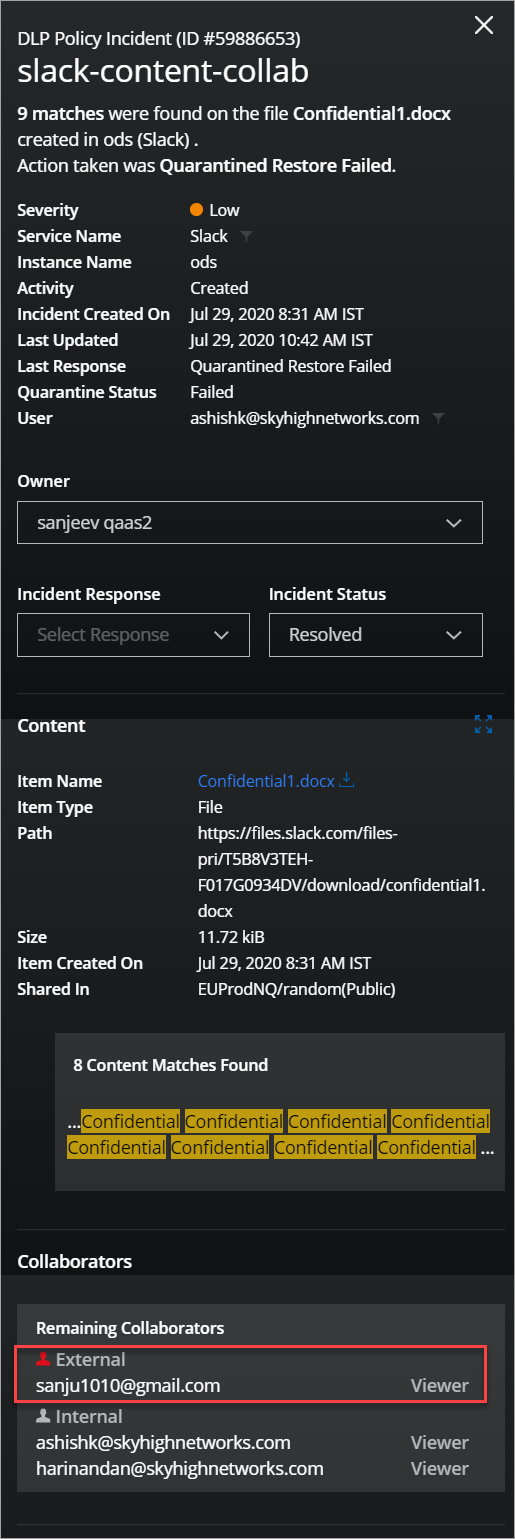
Here, the incident metadata displays the email ID of the guest/external user who joined the Slack channel. Also, displays the workspace name, channel name, and channel type.
