Skyhigh CASB Secure Topologies
The modular and stateless architecture provides the flexibility to configure Skyhigh CASB to work in different network topologies. As long as the connectivity between Skyhigh CASB and the Dictionary Server is preserved, and as long as this topology allows interception of the web traffic and routing, Skyhigh CASB functions properly. This flexibility provides customers with the ability to deploy Skyhigh CASB in multiple network architecture configurations, either on-premises or as a hosted service in the cloud.
In the typical on-premises deployment, servers reside in a trusted zone and are configured to intercept traffic that arrives from trusted users/clients. The trusted zone includes users that access Skyhigh CASB from within the organization network, remote users that use VPN to connect the organization users, Salesforce callouts that are sent from Salesforce into workstations that reside in the organization network, and emails that are generated within the Salesforce platform.
Topology 1
In the first topology scenario, all servers (Proxies, Key Server, Dictionary) are in a trusted zone. Web access (HTTP/HTTPS/SMTP) to Skyhigh CASB is allowed only from within the trusted zone or trusted origin (for example, Salesforce). This requirement can be enforced on the IP level.
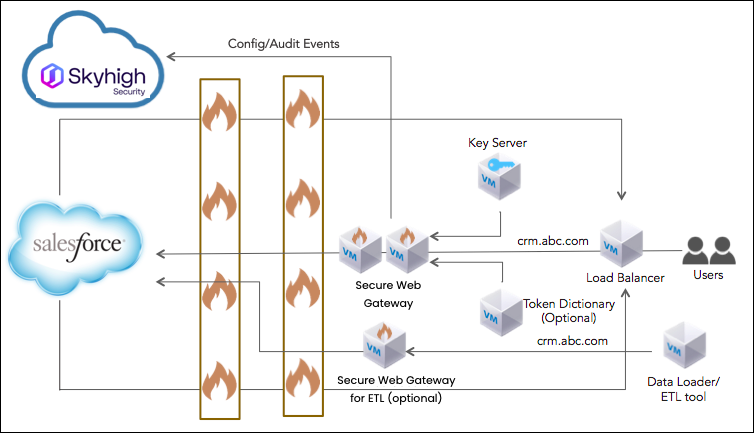
Example 1: Inbound (WAN to LAN)
Block any access from outside to Skyhigh CASB except the following:
- Responses to requests that originated from Skyhigh CASB (HTTP/HTTPS).
- Web-services callout (HTTP/HTTPS from Salesforce’s static IPs range to the proxies and only if the Skyhigh CASB implementation includes integration with web services).
- SMTP traffic (from Salesforce’s static IPs range to the Proxies and only if the Skyhigh CASB implementation includes integration with emails).
Example 2: Outbound (LAN to WAN)
Allow all access from Skyhigh CASB to the WAN (HTTP/HTTPS/SMTP)
- Remote/mobile users use VPN
- DNS configuration – can use either local or global DNS settings.
Note: Other ports must be opened to enable proper operation of Skyhigh CASB (mostly for internal communication of the Skyhigh CASB servers or for integration with external servers like the Token Dictionary or NFS server). For more details, go to the network requirement section.
Topology 2
Sometimes Salesforce/Skyhigh CASB implementation requires a topology that allows Skyhigh CASB to handle traffic originates from unknown origins, for example, mobile/remote users (the organization users that don’t use VPN), or customers/partners of the organization that need to have access to the customer org (like partners that need to access/post sensitive data on a customer portal).
In this case, our recommendation is to use the architecture that is presented below and place Skyhigh CASB servers in the DMZ.
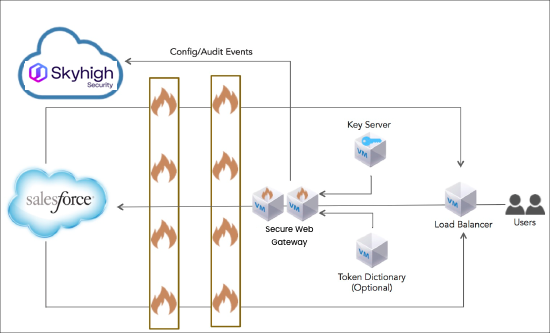
Other Considerations include:
- Skyhigh CASB Public IP. Required only if needed to intercept emails or Salesforce’s web-services callout. Use port-forwarding or a similar mechanism to route HTTP/HTTPS/SMTP traffic from the Skyhigh CASB CASB external IP address to the Proxy server’s internal IP addresses.
- DNS configuration. You can use either local or global DNS settings. Domains that are associated with Salesforce’s web-services callout and the Skyhigh CASB MX record must be registered publicly.
- Email. Emails sent from Salesforce into the organization are trusted and organizations can use the FW setting approach (Topology 1) to guarantee that the incoming email messages come from Salesforce.
Sometimes your Salesforce implementation requires that Skyhigh CASB accept email traffic that arrives from unknown sources (for example, Email-To-Case). In this case, customers usually prefer to route the email to the organization’s email gateway for vulnerability scanning and then route it to Skyhigh CASB. Emails sent from Salesforce using Skyhigh CASB's MX domain need to be routed to the organization mail gateway. That means Skyhigh CASB's MX record should point to the Email Gateway IP, and the organization’s mail gateway should be configured to route the Skyhigh CASB emails to the Skyhigh CASB proxies.
Load Balancers
Suitable for any topology, optional load balancers can be configured to maintain high availability. The load balancer should reside between the proxies for incoming requests from users, email, or web services callouts.
Platform Security Features
Another level of security can be achieved by enabling the following platform security features:
- TLS /Security for emails. Secure the email communication between Salesforce and Skyhigh CASB.
- Secure callouts. Uses a two-way SSL authentication between Salesforce callouts and your web services.
- File system. NFS (SAN/NAS).
- Token Dictionary.
