Allocating GRE Tunnels
You can filter web traffic from any site or location through a Generic Routing Encapsulatio (GRE) tunnel.
GRE tunneling encapsulates data packets within other packets. Endpoints are set up to directly send and receive GRE packets. Any routers or PoPs in between those two endpoints do not open the encapsulated packets; they only reference the headers surrounding the encapsulated packets in order to forward them.
To build GRE tunnels, you must configure:
- GRE tunnel mapping in Skyhigh CASB
- GRE tunnel interfaces on your networking device or in your SD-WAN service
GRE tunnel mapping
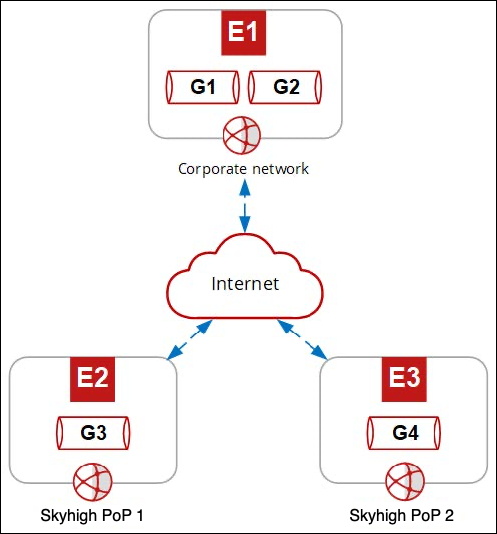
After you provide an external IP address, Skyhigh Security allocates two GRE tunnels on your internal network and provides the IP addresses needed to configure the GRE tunnel interfaces on your end.
Skyhigh Security allocates two GRE tunnels for redundancy:
- Primary GRE tunnel — Connects your network to the best point of presence in the cloud.
- Secondary GRE tunnel — Connects your network to the second-best point of presence in the cloud when the first point of presence isn't available.
View the allocated tunnels
After you save and publish the GRE tunnel mapping in Skyhigh CASB, you can view the allocated tunnels.
NOTE: You can edit the external source IP address. After editing it, make sure to save and publish.
Copy and save the IP addresses
You need these IP addresses to configure the GRE tunnel interfaces on your network device or in your SD-WAN service.
- GRE External Source IP — The public IP address that you provide (E1)
- Skyhigh PoPs — The domain names that you need to look up the public IP addresses of the primary and secondary points of presence based on the location of your network (E2 and E3)
- Internal Source IP — The source IP addresses that Skyhigh Security allocated on your network, one for each GRE tunnel (G1 and G3)
- Internal Destination IP — The destination IP addresses on the Skyhigh Security networks, one for each GRE tunnel (G2 and G4)