Traffic Flow in Skyhigh Secure Web Gateway and Cloud Firewall
Overview
This topic outlines the traffic flow between the endpoint client (Skyhigh Client Proxy) and both the Secure Web Gateway (SWG) and the Skyhigh Cloud Firewall. To access the Skyhigh Secure Service Edge (SSE) solution, we utilize a unified client known as the Skyhigh Client Proxy, also referred to as SCP. SCP enables users on Windows and macOS systems to connect and access both Web Gateway services and Cloud Firewall services. For details about SCP configurations (specifically for Cloud Firewall), see Client Proxy Set up For the First Time.
The Skyhigh Secure Web Gateway is a cloud-based web security solution that provides protection against various threats that may arise when users from any organization accessing web services through cloud environments.
Skyhigh Cloud Firewall is a cloud-based firewall solution converged with Skyhigh Security Service Edge to aggregate traffic from various sources that employ differing security postures. Skyhigh Cloud Firewall offers a multi-layered protection and performs deep packet inspection, allowing organizations with greater visibility, granular policy enforcement, and control over the applications to counter web-based threats.
The Traffic Flow in Skyhigh Security Service Edge
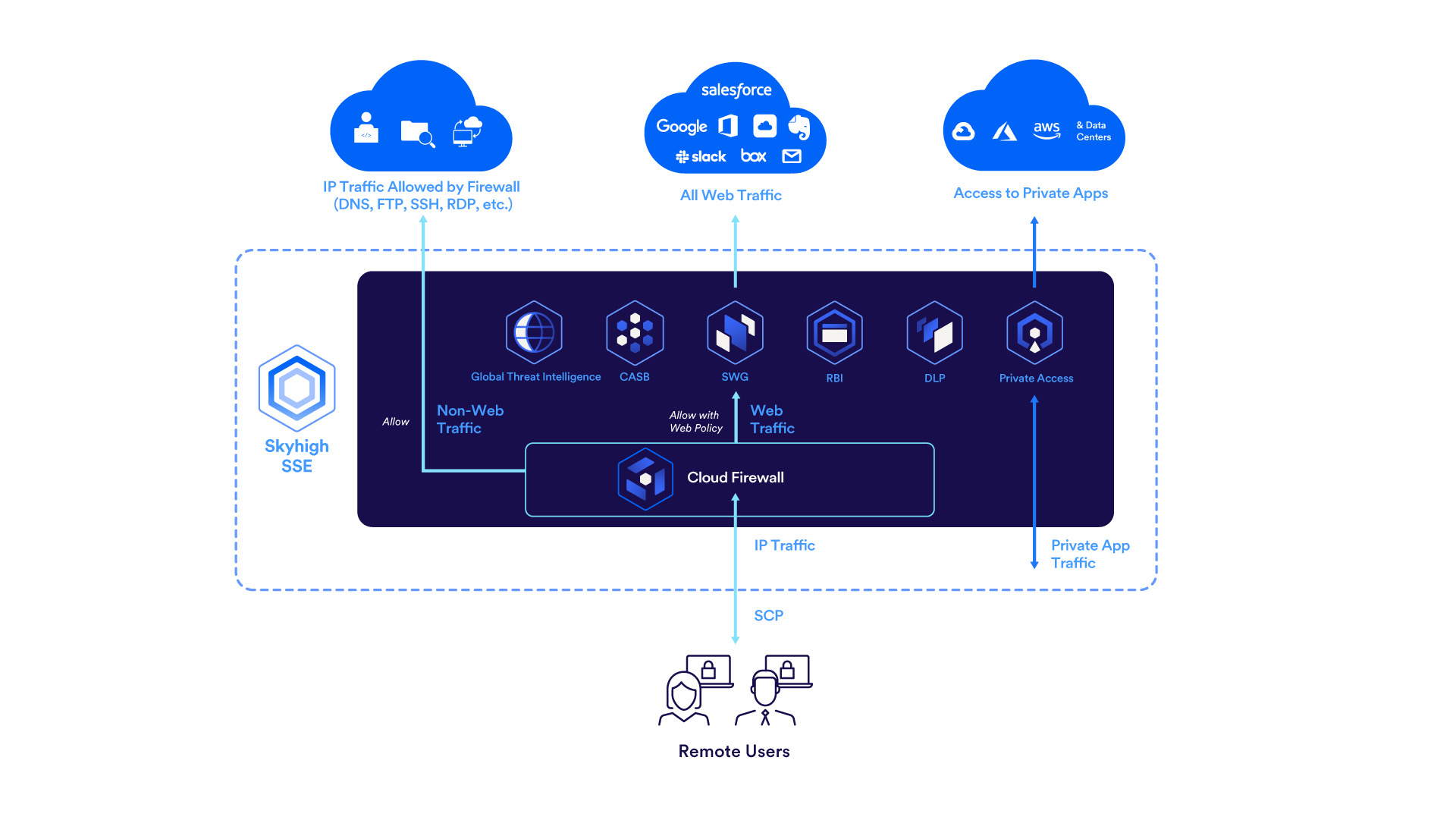
Skyhigh Secure Web Gateway
Use Case 1: The End User has a license for both Secure Web Gateway and Cloud Firewall
In this scenario, when the end-user attempts to access the web and generates HTTP/HTTPS traffic, below are the detailed steps that the traffic follows::
- The Skyhigh Client Proxy installed on the end-user system encrypts the traffic and then sends it to the Cloud Firewall.
NOTE: The traffic directed to the Cloud Firewall is subject to SCP policies, which may intercept and redirect it through the Secure Web Gateway as necessary.
- This traffic is encrypted and sent to the Cloud Firewall module through a Wireguard tunnel.
- The Cloud Firewall module decrypts the traffic and inspects it. It performs Deep Packet Inspection on the packet header.
- After inspecting the header, the Cloud Firewall module identifies the traffic as web traffic and redirects it to the Secure Web Gateway module
- The Secure Web Gateway module does the rest and sends the traffic to the intended destination.
Use Case 2: The End User has a license for only Secure Web Gateway and NOT for Cloud Firewall
In this scenario, whenever the end-user tries to access the web and generates HTTP/HTTPs traffic, the Skyhigh Client Proxy simply forwards the traffic to the Secure Web Gateway module and the SWG module does the rest. Note that there is no involvement of the Cloud Firewall.
Skyhigh Cloud Firewall
Whenever the end-user generates Non HTTP/HTTPs traffic,
- The Skyhigh Client Proxy encrypts the traffic and forwards it to the Cloud Firewall through a tunnel.
- Upon receiving the packet, the Cloud Firewall decrypts it and begins inspection, focusing initially on the packet header only.
- After inspecting the packet header, it identifies the traffic as non-HTTP/HTTPs and proceeds with Deep Packet Inspection of the entire packet.
- Once the results of the Deep Packet Inspection are satisfactory, the Cloud Firewall forwards the traffic to its destination.
Points to Remember
- For web traffic, Deep Packet Inspection is performed on the first packet only if the customer has a license for Cloud Firewall. Once the first packet is inspected and determined to be HTTP/HTTPS, subsequent packets related to it are not inspected and are forwarded to the web proxy. However, for non-web traffic passing through the Cloud Firewall, Deep Packet Inspection is conducted on the entire packets to ensure overall security.
To view additional configuration examples, see Firewall Rule Configuration Examples.
