Blocking the Download of a Virus-infected File
The anti-malware filtering functions of Secure Web Gateway protect your network against infections from the web.
An infection might be imported, for example, when a user who works inside this network attempts to download a virus-infected file from a web server.
The infection is detected when the file is intercepted and scanned on Secure Web Gateway.
According to a web security rule, the download is blocked and the user who requested the download is notified.
NOTE: Blocking the download of a virus-infected file is performed by default on Secure Web Gateway, so no administrator activities are required. You can, however, modify the default process.
- Working with a web browser that is configured to run as a client of Secure Web Gateway, a user clicks a link on a webpage to request the download of a file from a web server.
- The request is processed.
- The request is redirected to Secure Web Gateway.
- The request is processed in the request cycle on Secure Web Gateway.
The web security rules that are enabled for this cycle are processed to see if they apply.
The request might not be compliant with your web security policy, which means at least one rule applies that forbids forwarding this request to the web.
- Because no rule in the request cycle applies, Secure Web Gateway forwards the request to the web server.
- The web server accepts the request and sends the file that the user wants to download in response.
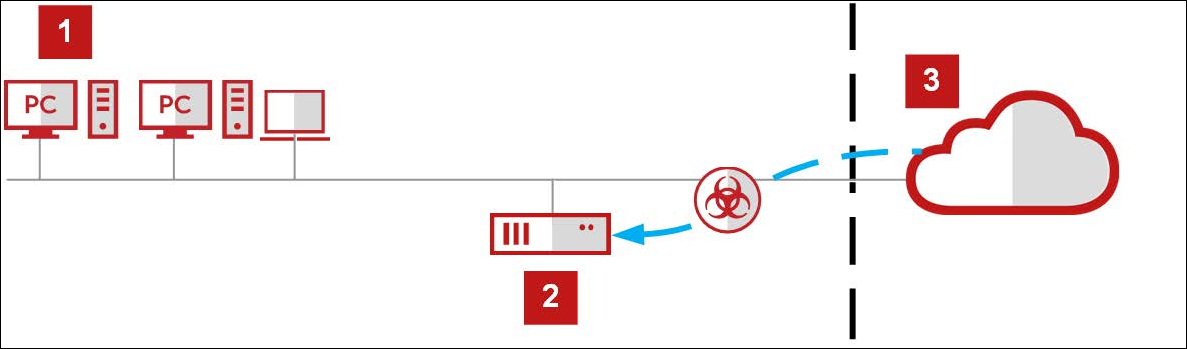
1 - Your network, 2 - Secure Web Gateway, 3 - Web
- The response is processed.
- The response arrives at Secure Web Gateway.
- The response is processed in the response cycle of Secure Web Gateway.
The web security rules that are enabled for this cycle are processed to see if they apply.
These rules include the following rule, which is part of the default rule set for anti-malware filtering:
Antimalware.Infected<Gateway Anti-Malware> equals true –> Block<Virus Found> — Statistics.Counter.Increment (“BlockedByAntiMalware”,1)<Default>
In plain text, this rule says that a virus-infected web object must not be forwarded to your network in response to a download request that a user submitted.
- The rule applies if its criteria matches. To find out if this is the case, the following substeps are performed.
- The value for the Antimalware.Infected property is determined. If this value is true, the criteria matches.
To determine the value, the anti-malware engines that are licensed and enabled process the response. The URL and the response header are checked and the file that was sent as the body of the response is scanned.
Enabling or disabling these engines is part of configuring the Gateway Anti-Malware settings, which are shown as applicable after the property name in the rule.
The following engines are enabled by default (if licensed):- Anti-Malware engine (included in the license for Secure Web Gateway)
- Gateway Anti-Malware engine (GAM engine, requires a separate license)
A third anti-malware engine, the Avira engine, can also be enabled (included in the license for the GAM engine).
- The result of scanning the file is that it is virus-infected. So the value of the Antimalware.Infected property is set to true, which means that the rule criteria matches.
- The value for the Antimalware.Infected property is determined. If this value is true, the criteria matches.
- Because the criteria matches, the rule action, which is Block, is executed.
- Rule processing is stopped for all other rules on Secure Web Gateway.
A rule already blocks the download, so there is no need to try out any other rules and see if they also block it. - The virus-infected file is not forwarded to the user's browser.
- A block message is sent to this browser instead.
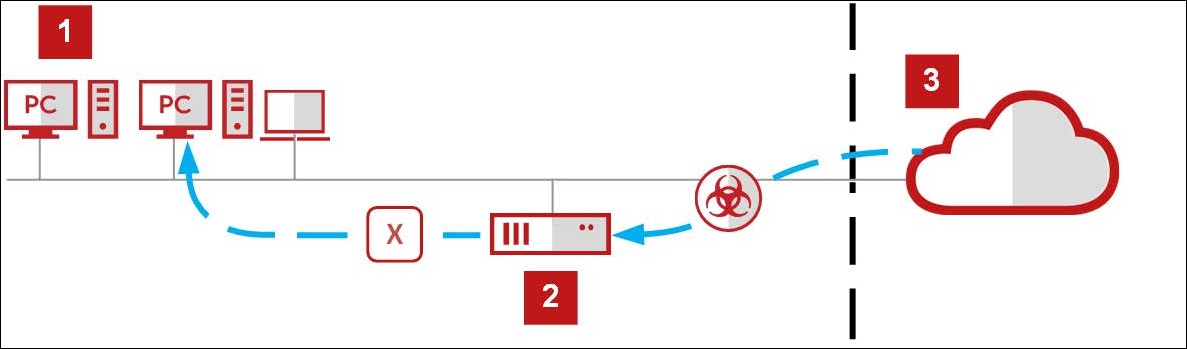
1 - Your network, 2 - Secure Web Gateway, 3 - Web
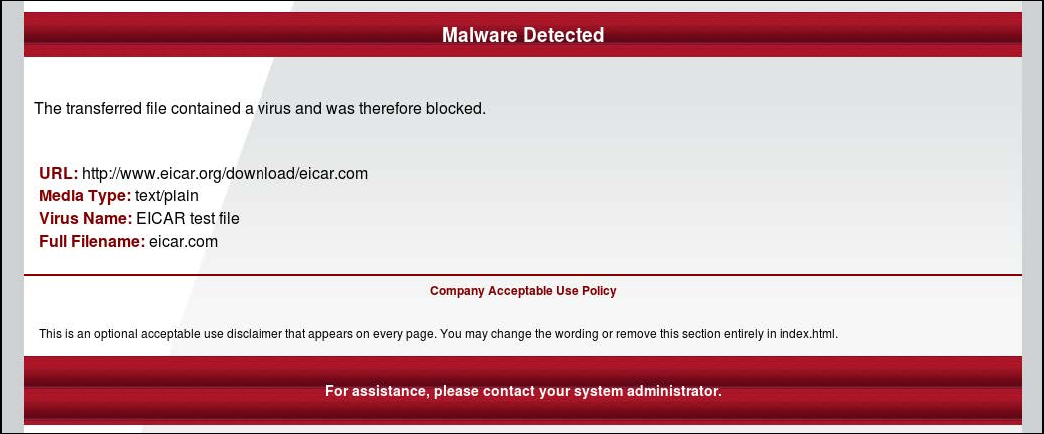
This message notifies the user that downloading the requested file was blocked because this file was virus-infected.
The text and layout of the message can be edited by configuring the Virus Found settings, which are shown after the action name in the rule.
- The Statistics.Counter.Increment event increases the counter for blocking caused by anti-malware filtering.
- Rule processing is stopped for all other rules on Secure Web Gateway.
- The block message appears in the browser that the user works with.
The following is an example of a block message in English language.